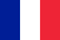
Among all pathological processes affecting the spine in its various parts, cervical osteochondrosis is considered one of the most common. This disease leads to many complications, mainly because it affects the spinal cord and also negatively affects the functioning of the brain.
According to the statistics for 2017, the disease is significantly younger. If previously osteochondrosis mainly affected people after the age of 40, today various stages of cervical osteochondrosis are diagnosed in 90% of people over the age of 25. For this reason, it is important to know as much as possible about the pathology, from what it is to treatment methods.
What is cervical osteochondrosis?
In medical practice, the words cervical osteochondrosis mean an acquired progressive disease that affects a certain part of the spine. This pathological process is characterized by degenerative-dystrophic processes in the tissues of the intervertebral discs, which are shock absorbers for the cervical vertebrae.
Degenerative-dystrophic changes in the intervertebral discs are caused by the fact that they are worn and deformed. As a result, the distance between the vertebrae is reduced and as a result the following consequences occur:
- Narrowing of the spinal canal in certain areas of the spine.
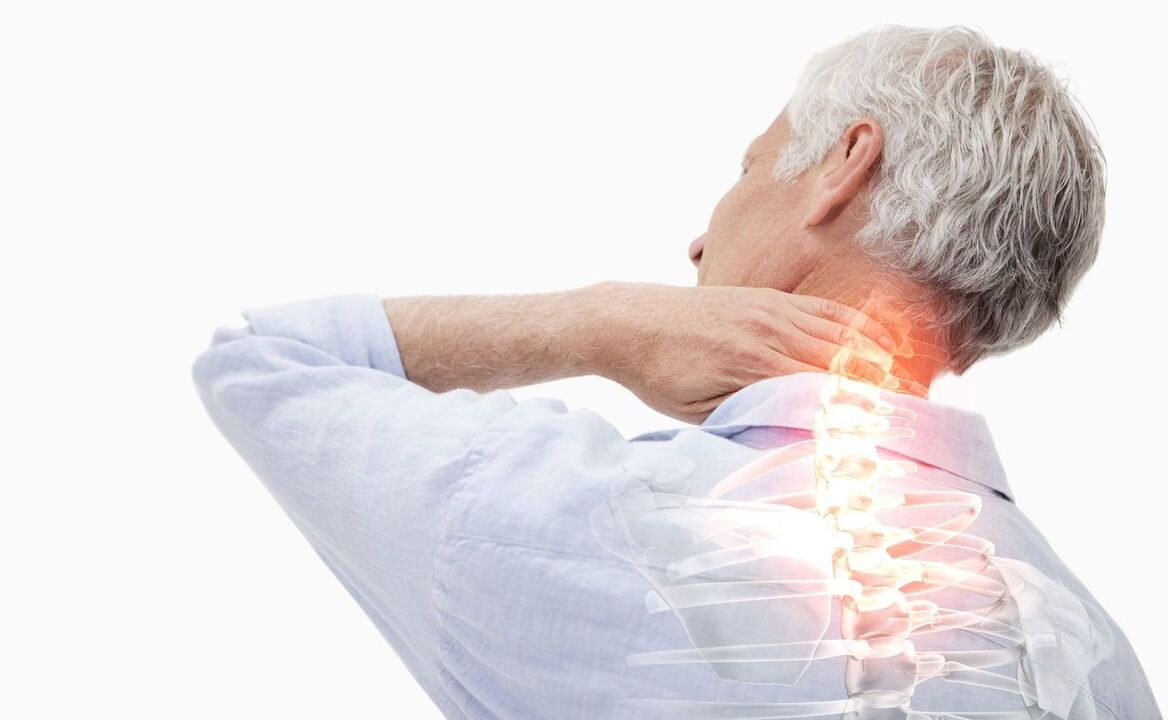
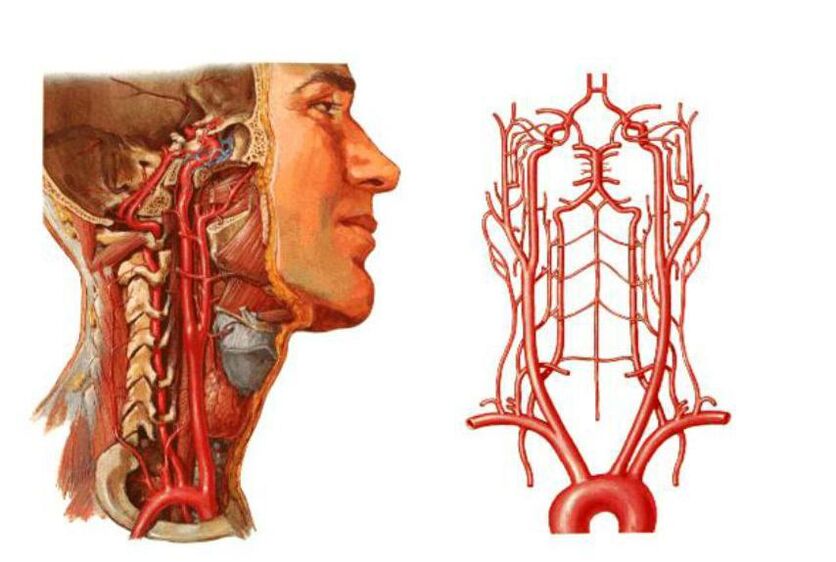
- Compression of the vertebral arteries - large blood vessels that provide blood supply to the brain. Because of this, the supply to the brain deteriorates and blood circulation in the cervical spinal cord is impaired.
- Intervertebral discs can become deformed and flattened. This leads to compression of certain areas of the spinal cord and nerves, with the most common compression of the nerve roots.
All these problems threaten not only impaired blood circulation in the brain, neck pain, headaches, etc. The development of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is dangerous with neurological problems, deterioration of the central nervous system and damage to brain tissue.
According to the international classification of diseases, osteochondrosis of the cervical vertebrae is determined by several separate codes. The disease code according to ICD 10 depends on the age at which the disease was diagnosed:
- M02 – dystrophy of the intervertebral discs in adolescence.
- M42. 12 – degenerative process in the neck area in adults.
Many factors depend on the age of the patient and the degree of development of the pathological process, for example, the consequences, complications, symptoms and, of course, the principles of treatment.
reasons
Knowing the reasons for the development of cervical osteochondrosis can play a decisive role in the diagnostic process, as well as in determining the principles of combating the disease.
However, before listing the reasons, it is worth saying that doctors identify two factors that lead to the development of this pathological process:
- Pathological - the destruction of intervertebral discs and other spinal structures with the participation of nearby tissues, vessels and nerve bundles in the pathological process occurs under the influence of adverse external factors. The more severe these factors and other pathologies are, the faster the disease develops.
- Physiological - the development of pathology is primarily based on age-related changes. We are talking about the natural aging of the cartilage tissue of the spine, the deposition of salts, etc.
If we list more specific causes of cervical osteochondrosis, they are as follows:
- Disorders of metabolic processes in the body, as well as certain stages of obesity.
- Lack of physical activity is a phenomenon characterized by limited mobility. We're not just talking about injuries or illnesses, it also includes sedentary lifestyles and sedentary jobs.
- Pathologies of the cardiovascular system, which contribute to impaired blood circulation in the brain, changes in pressure, etc.
- Improper posture includes various forms of scoliosis, rheumatism and even flat feet.
- Trauma of the cervical spine. In this case, we are talking about sprains, bumps, bruises. Injuries to other parts of the spine can affect the development of cervical osteochondrosis.
- Excessive physical load on the cervical vertebrae, caused by intense sports or severe physical difficulties, depending on the type of activity of the person.
- A sedentary lifestyle is also dangerous due to constant tension in the cervical vertebrae and the entire spine if you sit incorrectly or on uncomfortable furniture.
- Hernia of the cervical vertebrae, as well as various concomitant diseases.
- Forcefully holding the head for a long time in an uncomfortable or unnatural position. In this case, not only muscle tension occurs, but also the spine in the cervical region is bent.
- Doctors believe that constant stress and nervous tension are a very common cause.
- One of the causes is also considered to be congenital anomalies in the structure of the spine.

What health hazards does it pose?
As mentioned earlier, the cervical spine contains not only the spinal cord and various nerve branches, but also the vertebral arteries that supply blood to the back of the brain, the cerebellum, and the medulla oblongata.
With the development of cervical osteochondrosis, nearby tissues become inflamed. In addition, the development of the pathology threatens to compress the nerve roots and squeeze the blood vessels, the consequences of which are as follows:
- Osteochondrosis is accompanied by deformations of the spine, which leads to a narrowing of the spinal canal in certain areas. This can lead to compression of the spinal cord and nerve branches, which promises serious neurological problems. In severe cases, a person experiences pain and even has the possibility of losing control over certain parts of the body (mainly in the hands or face).
- Compression of the vessels of the neck, as already mentioned, is accompanied by impaired circulation in the occipital region of the brain. In this case, the brain stops receiving oxygen and nutrients in the necessary quantities and oxygen starvation begins. If blood circulation is impaired, there is a real risk of ischemic stroke and various neurological pathologies.
Syndromes
Speaking of the danger that cervical osteochondrosis poses, as it progresses and in the absence of appropriate treatment, the disease can lead to a number of complications and syndromes.
The main syndromes are:
- Vertebrates.
- Vertebral artery.
- Koreshkovy.
- Hearty.
It is important to know that each of these symptoms is accompanied by painful sensations of a different nature, as well as numerous adverse clinical signs. A person may feel dizzy, have tinnitus and many more.
Vertebral syndrome
It speaks of a direct connection between cervical osteochondrosis and bone-cartilaginous tissues. The symptoms of this type of pathology are also associated with damage to the mentioned tissues:
- Neck movements are partially or completely restricted.
- Head movements are accompanied by painful sensations in the neck.
- X-ray shows morphological changes in tissues (intervertebral and vertebral bodies).
It is worth noting that vertebral syndrome is always accompanied by these three clinical signs. If at least 1 of them is missing, the diagnosis will be completely different.
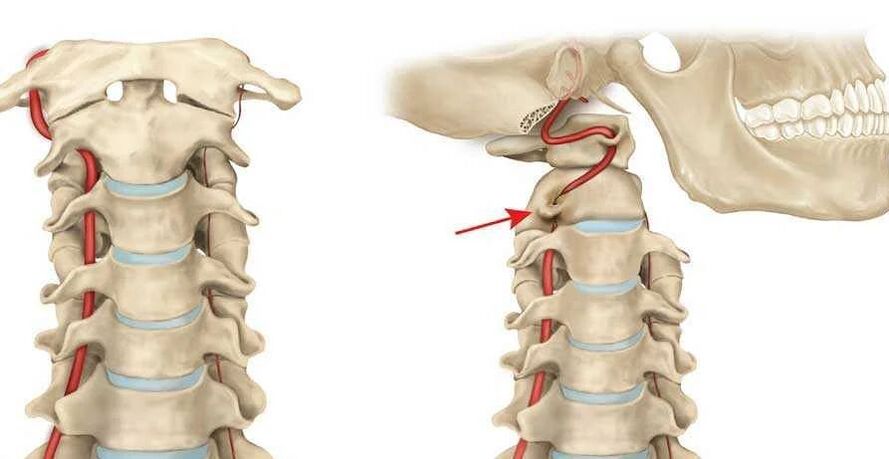
Vertebral artery syndrome
This syndrome is caused by a narrowing of the vertebral artery, which leads to vestibular, vascular and autonomic problems. In this case, the main symptoms are extensive:
- Headache and migraine.
- Visual impairments.
- Noises in the ears.
- Frequent dizziness and many others.
The most dangerous symptom is fainting, which indicates a severe lack of oxygen.
Radicular syndrome
It occurs when the roots of the spinal cord are damaged. In this case, the nerve conduction is disturbed, a person may feel pain or lose sensitivity in certain parts of the body or even suffer from paralysis.
Depending on which of the 8 radicular pairs a conduction disorder occurs, the following symptoms are identified:
- 1 pair - numbness or pain in the back of the head;
- 3rd pair – impaired chewing reflex, numbness of the tongue and unpleasant sensations behind the ears;
- 4 pairs – pain in the collarbone area, impaired swallowing reflex;
- 5 pair - disorders of the shoulder girdle, accompanied by problems with the movement of the hands;
- 6th pair - the patient begins to feel pain and numbness in the forearm and shoulder blades;
- 7th pair - hands and fingers (usually index and middle) are numb;
- 8th pair - problems similar to the previous point, but numbness is felt in the ring finger and little finger.
Based on the described characteristics, it is sometimes possible to determine which pair of roots is affected by radicular syndrome.
Cardiac syndrome
Despite the fact that the pathological process is still localized in the cervical vertebrae, the syndrome has all the signs of cardiac pathologies. The clinical picture is as follows:
- Fast pulse.
- Pain in the sternum.
- Shortness of breath, weakness, lethargy, reduced work capacity.
Degree of development of the disease
When we talk about the degree of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, we mean the stages of progression of the pathological process, which differ in clinical signs. In total, there are four stages of disease development:
- The first stage is characterized by vague symptoms. Patients complain of a slight headache, during the initial examination the doctor notes a slight degree of muscle stiffness.
- Pain in the cervical spine and head is more frequent, more intense and radiates to the shoulder and arms. The pathology is caused by damage to the intervertebral discs and pinching of the nerve roots. The pain increases when turning the head, throwing back and bending forward.
- In the third stage, the pain is constant, muscle weakness is noted in the arms and hernias are formed in the intervertebral discs. Movements in the neck area are limited, there is frequent dizziness.
- The fourth stage is accompanied by complete destruction of the intervertebral disc, cartilage tissue is replaced by connective tissue. In addition to pain and vertigo, coordination problems are observed, and spinal arteries are often compressed.
Signs and symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis
In order to consult a doctor in a timely manner, it is necessary to clearly understand the signs of cervical osteochondrosis. In some cases, such knowledge allows you to seek help in the initial stages of the disease, when it is easier to treat.
In general, the symptoms of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine are as follows:
- Pain in osteochondrosis is always present, only the intensity and frequency are different. Pain is the first clinical sign. Their intensity depends on the stage of disease progression, they are dull or compressive in nature. Painful sensations appear mainly in the neck and occipital region, but can also radiate to the temporal region, shoulder girdle and arms.
- In most cases, there are manifestations of damage to the vestibular apparatus. We are talking about frequent unexplained dizziness, nausea, poor coordination of movements, uneven gait, loss of space.
- One of the most common clinical signs is stiffness of the neck muscles and stiffness of movements. It is difficult for a person to turn, lower and throw back his head, the movements are accompanied by attacks of pain.
- Many patients report a sensation of "goosebumps" on the scalp or a characteristic tingling sensation.
- Muscle weakness and numbness appear in the arm area.
- There are often psychological manifestations expressed in depression, drowsiness, sudden changes in mood, short temper or irritability.
- Due to poor blood circulation and damage to brain tissue, dizziness increases and tinnitus appears, similar to rustling, pulsation and ringing.
- Most patients note a deterioration of vision, as well as pain in the eyeballs, especially when they try to squint their eyes too much to the left, right, up or down.
Sometimes it is possible to determine the degree of development of the pathological process by symptoms. But for a complete diagnosis, this is still not enough, and a number of diagnostic measures are required.
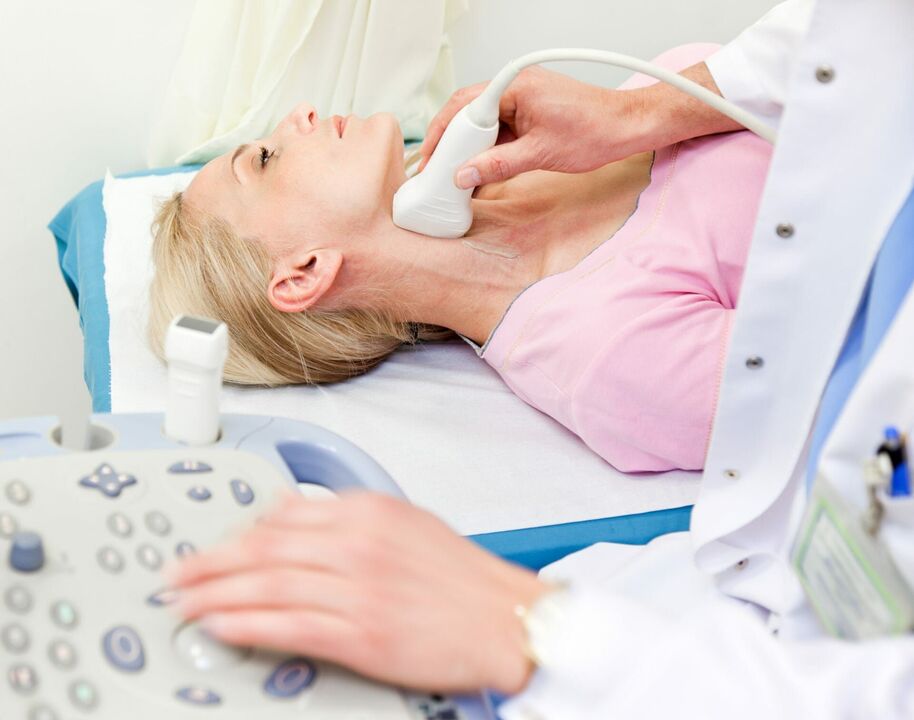
Diagnostic methods
The diagnosis of cervical osteochondrosis is necessary to determine the location and stage of disease progression. The following diagnostic methods are required for a complete diagnosis:
- Radiography is the main method for determining the degree and localization of spinal deformity.
- Computed tomography can be used to more accurately diagnose pathological changes in the vertebrae and intervertebral discs.
- MRI (nuclear magnetic resonance) - enables a detailed study of discs and vertebrae, determining the presence of hernias, protrusions, the degree of lesions, etc.
- Dopplerography - with this study, it becomes possible to find the place of compression of the artery and assess the degree of circulatory disorders.
Methods of treatment
Treatment of osteochondrosis of the neck always includes an integrated approach. The principles of treatment depend on many factors, such as the age of the patient, the stage of development of the disease, the severity of the clinical picture, etc.
However, in this situation, you cannot do without a doctor, and first of all, you can contact a general practitioner, who will then refer you to a vertebrologist.
As for the integrated approach: osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is treated with the help of drug therapy, physiotherapy, massages, exercises and other methods, which are worth talking about in more detail.
Medication treatment
The basis for the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis is drug therapy, which includes the use of tablets, drugs and drugs from the following groups:

- Pain relievers - analgesics and antispasmodics. The first directly dull the nerve centers, thereby relieving painful sensations. The latter allow you to relieve the spasm of the neck muscles, improving blood flow and suppressing pain.
- NSAIDs - non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are necessary to reduce inflammation, most of them also eliminate pain. Often these drugs are used in the form of gels or ointments that are rubbed into the affected area.
- Muscle relaxants are another way to relieve muscle spasms in the cervical region.
- Chondroprotectors are mandatory at certain stages of osteochondrosis of the spine, as they contribute to the restoration of bone tissue.
- Vitamins of group B - normalize the metabolic processes of nervous tissue, improve the conduction of nerve impulses and promote the functioning of the central nervous system.
Remember that the treatment should be carried out only under the supervision of a doctor who is responsible for prescribing each drug, as well as for determining the duration of use and dosage.
Physiotherapy
Treatment of osteochondrosis of the neck will be many times more effective with the help of certain physiotherapeutic techniques:
- Electrophoresis.
- Laser therapy.
- Ultrasound.
- Massage.
Massage therapy must be performed by an experienced medical specialist, the treatment is carried out in a course of at least 10 sessions. Cervical massages help to normalize blood circulation, restore elasticity, muscle tone, relieve pain, etc.
Physiotherapy
Therapeutic exercises also help speed up recovery, but are only done during the recovery stages. It is important that the exercises do not bring discomfort or pain to the patient. Exercise therapy is aimed at strengthening muscles and relieving discomfort during movements by increasing the elasticity of muscle fibers.
The exercise technique is initially developed by a physiotherapist, after which the patient can independently perform gymnastics at home.
Manual therapy
Manual therapy is based on the principle of restoring motor functions and mobility between the vertebrae. Initially, the manipulations consist of a light relaxing massage, then the doctor applies more and more force, exerting pressure and turning the neck to the vertebrae.
Kuznetsov applicator
The use of Kuznetsov applicators is one of the methods of treatment of spinal diseases, including osteochondrosis. The impact of the device on the cervical vertebrae normalizes metabolic processes, relieves pain, increases muscle tone, improves blood circulation, increases the conductivity of nerve tissue, etc.
Treatment at home
The whole range of therapeutic measures is carried out at home, with the exception of physiotherapy, massages (in some cases) and the first stages of exercise therapy. However, now we are talking about traditional medicine and we will look at a few of the most effective recipes:
- To use horseradish - take a leaf of this plant, pour boiling water over it and apply it to the inside of your neck, securing it with a bandage. It can be left on while you sleep to enhance the effect.
- If there are no contraindications from a doctor, warming up the cervical vertebrae will be a good remedy. The simplest way is to use pepper, but you can heat the wax comb by applying it 1-2 times until it cools completely.
Disease prevention
To prevent the development of the disease or its return after treatment, it is necessary to prevent osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. It consists of the following simple recommendations:
- Sleep on a flat, hard surface, it is better to buy a special orthopedic mattress and a pillow that takes the shape of your head.
- To prevent the disease, monitor your physical activity and do not overload the spine. If you must lift weights, do so smoothly and keep your back straight.
- If your job requires you to sit for long periods of time, take breaks. Every hour you should walk or stretch your stiff muscles with simple gymnastic movements.
To prevent osteochondrosis, it is useful to swim and hang on the horizontal bar for 2-3 minutes every day.